목차
nmon 이란
Nigel's Performance Monitor for Linux on POWER, x86,x86_64, Mainframe & now ARM(Raspberry Pi)의 약자이다.
시스템 성능모니터링을 위해 사용하는 무료 툴이다. nmon은 두가지 형태의 output을 준다.
한가지 방식은 스크린에 모니터링 정보를 display 해 주는 방식이고
다른 하나는 콤마로 구분된 정보를 파일로 저장해 주는 방식이다.
이는 다른 툴을 사용해 활용 가능항 정보로 만들 수 있다.
nmon 설치
아래 사이트에서 플랫폼에 적합한 binary 파일을 다운 받아서 서버에 업로드하면 된다.
nmon 실행
설치한 실행파일(업로드한 바이너리 파일)을 실행하면된다.
아래는 nmon 실행 화면이며 화면을 통해 정보를 제공하는 방식이다.
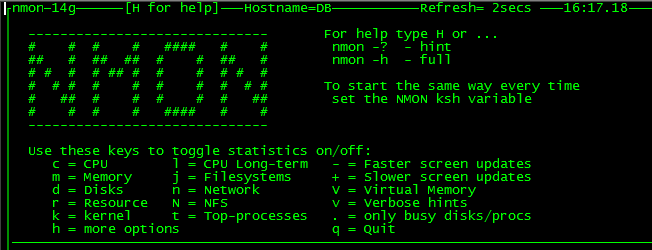
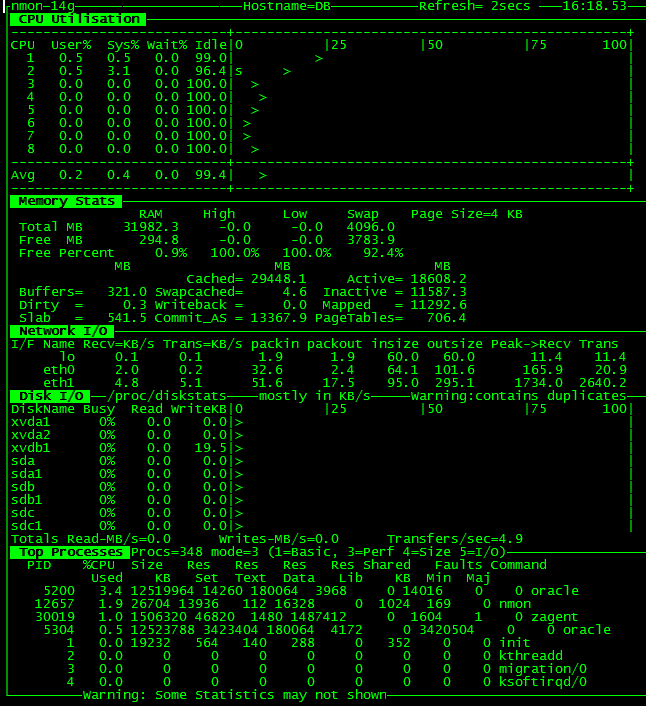
nmon Help 화면
DB-testVM:/stg/oracle/> nmon -h
Hint: nmon [-h] [-s <seconds>] [-c <count>] [-f -d <disks> -t -r <name>] [-x]
-h FULL help information
Interactive-Mode:
read startup banner and type: "h" once it is running
For Data-Collect-Mode (-f)
-f spreadsheet output format [note: default -s300 -c288]
optional
-s <seconds> between refreshing the screen [default 2]
-c <number> of refreshes [default millions]
-d <disks> to increase the number of disks [default 256]
-t spreadsheet includes top processes
-x capacity planning (15 min for 1 day = -fdt -s 900 -c 96)
Version - nmon 14g
For Interactive-Mode
-s <seconds> time between refreshing the screen [default 2]
-c <number> of refreshes [default millions]
-g <filename> User Defined Disk Groups [hit g to show them]
- file = on each line: group_name <disks list> space separated
- like: database sdb sdc sdd sde
- upto 64 disk groups, 512 disks per line
- disks can appear more than once and in many groups
-b black and white [default is colour]
example: nmon -s 1 -c 100
For Data-Collect-Mode = spreadsheet format (comma separated values)
Note: use only one of f,F,z,x or X and make it the first argument
-f spreadsheet output format [note: default -s300 -c288]
output file is <hostname>_YYYYMMDD_HHMM.nmon
-F <filename> same as -f but user supplied filename
-r <runname> used in the spreadsheet file [default hostname]
-t include top processes in the output
-T as -t plus saves command line arguments in UARG section
-s <seconds> between snap shots
-c <number> of snapshots before nmon stops
-d <disks> to increase the number of disks [default 256]
-l <dpl> disks/line default 150 to avoid spreadsheet issues. EMC=64.
-g <filename> User Defined Disk Groups (see above) - see BBBG & DG lines
-N include NFS Network File System
-I <percent> Include process & disks busy threshold (default 0.1)
don't save or show proc/disk using less than this percent
-m <directory> nmon changes to this directory before saving to file
example: collect for 1 hour at 30 second intervals with top procs
nmon -f -t -r Test1 -s30 -c120
To load into a spreadsheet:
sort -A *nmon >stats.csv
transfer the stats.csv file to your PC
Start spreadsheet & then Open type=comma-separated-value ASCII file
The nmon analyser or consolidator does not need the file sorted.
Capacity planning mode - use cron to run each day
-x sensible spreadsheet output for CP = one day
every 15 mins for 1 day ( i.e. -ft -s 900 -c 96)
-X sensible spreadsheet output for CP = busy hour
every 30 secs for 1 hour ( i.e. -ft -s 30 -c 120)
Interactive Mode Commands
key --- Toggles to control what is displayed ---
h = Online help information
r = Machine type, machine name, cache details and OS version + LPAR
c = CPU by processor stats with bar graphs
l = long term CPU (over 75 snapshots) with bar graphs
m = Memory stats
L = Huge memory page stats
V = Virtual Memory and Swap stats
k = Kernel Internal stats
n = Network stats and errors
N = NFS Network File System
d = Disk I/O Graphs
D = Disk I/O Stats
o = Disk I/O Map (one character per disk showing how busy it is)
o = User Defined Disk Groups
j = File Systems
t = Top Process stats use 1,3,4,5 to select the data & order
u = Top Process full command details
v = Verbose mode - tries to make recommendations
b = black and white mode (or use -b option)
. = minimum mode i.e. only busy disks and processes
key --- Other Controls ---
+ = double the screen refresh time
- = halves the screen refresh time
q = quit (also x, e or control-C)
0 = reset peak counts to zero (peak = ">")
space = refresh screen now
Startup Control
If you find you always type the same toggles every time you start
then place them in the NMON shell variable. For example:
export NMON=cmdrvtan
Others:
a) To you want to stop nmon - kill -USR2 <nmon-pid>
b) Use -p and nmon outputs the background process pid
c) To limit the processes nmon lists (online and to a file)
Either set NMONCMD0 to NMONCMD63 to the program names
or use -C cmd:cmd:cmd etc. example: -C ksh:vi:syncd
d) If you want to pipe nmon output to other commands use a FIFO:
mkfifo /tmp/mypipe
nmon -F /tmp/mypipe &
grep /tmp/mypipe
e) If nmon fails please report it with:
1) nmon version like: 14g
2) the output of cat /proc/cpuinfo
3) some clue of what you were doing
4) I may ask you to run the debug version
Developer Nigel Griffiths
Feedback welcome - on the current release only and state exactly the problem
No warranty given or implied.
nmon 배치모드
위 Help 화면의 명령어를 사용해 아래와 같이 배치모드, 즉 콤마로 구분된 정보를 파일에 저장할 수 있다.
nmon -f -m /home/oracle/nmon -s2 -c 300
일반적인 사용방법으로 cron에 등록을 해 정보를 저장하는 방식을 추천한다.
10초 단위로 하루를 기록할 경우 아래의 내용으로 cron에 등록하면 된다.
0 0 * * * /home/oracle/nmon -f -m /home/oracle -s 10 -c 43195
nmon analyzer 사용
아래 링크에서 nmon analyzer 엑셀 파일을 받을 수 있다.
아래는 nmon analyzer을 통해 생성한 그래프에 대한 예제이다.
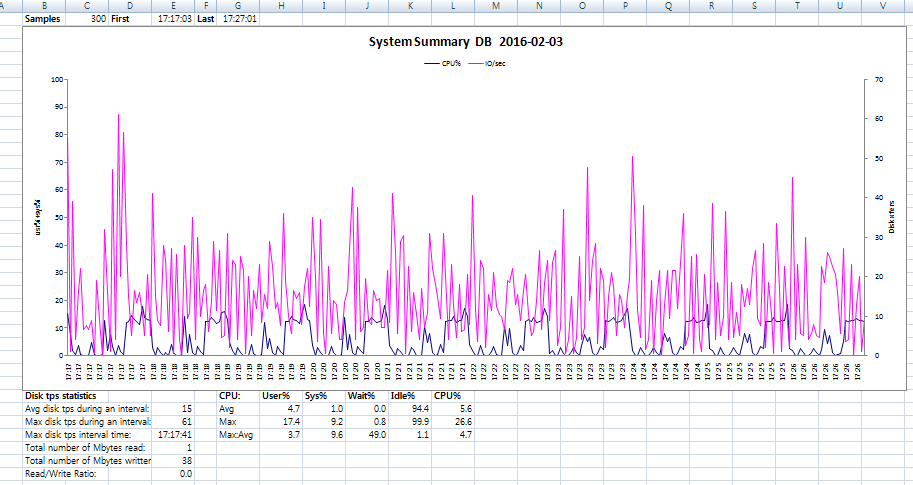
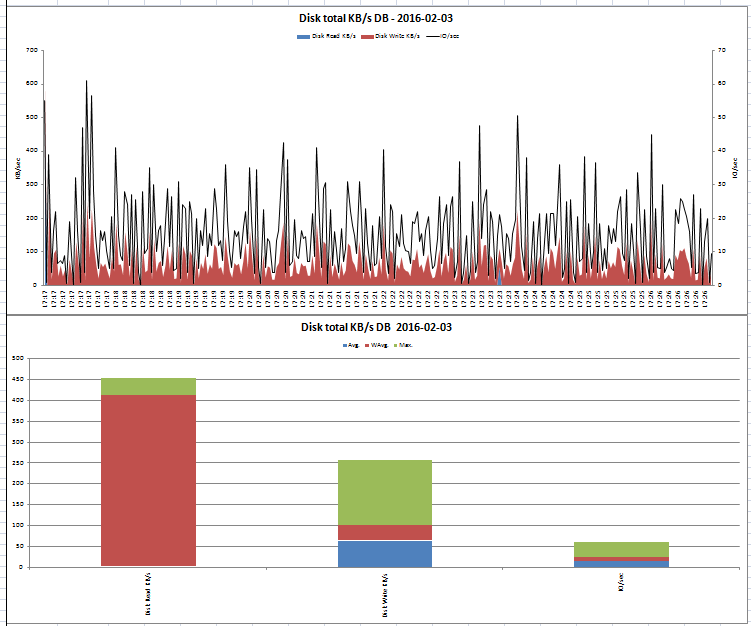
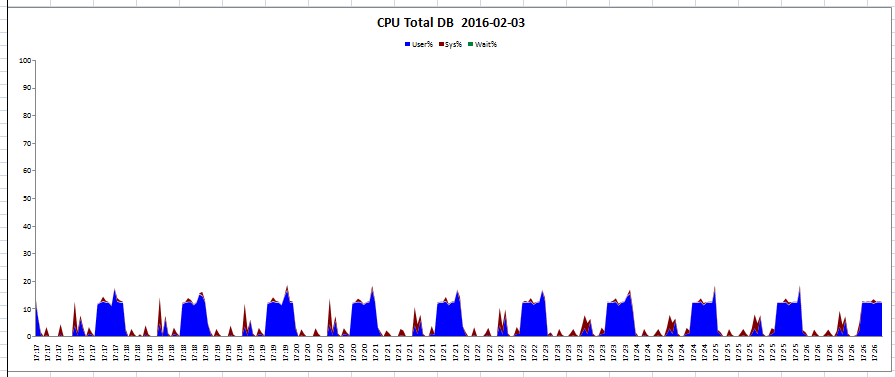
위 내용은 일부 항목이며 많은 내용이 시트별로 저장된다.
nmonchart 사용
nmon analyzer와 비슷한 용도로 사용 가능한 툴이며 아래와 같은 같이 사용하여 html 형태의 output을 받을 수 있다.
nmonchart DB_160203_1717.nmon DB_160203_1717.html
DB_160203_1717.nmon은 배치모드를 통해 얻은 콤마로 구분된 내용이 들어있는 파일이며
DB_160203_1717.html은 output 파일입니다.
아래는 output 파일의 일부 내용이다.
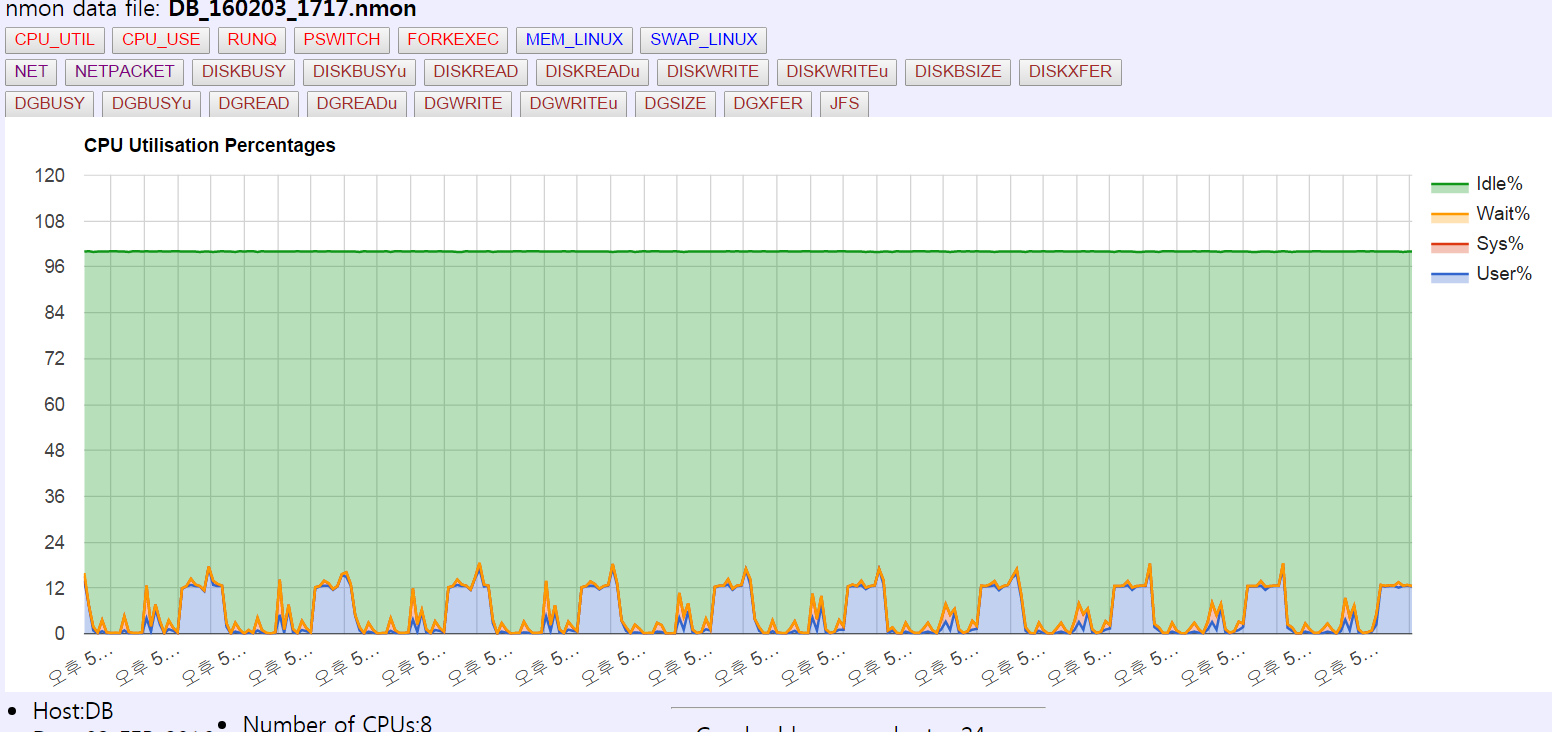
아래 링크는 예제 파일의 출력파일이다.
http://nmon.sourceforge.net/docs/sampleC.html
